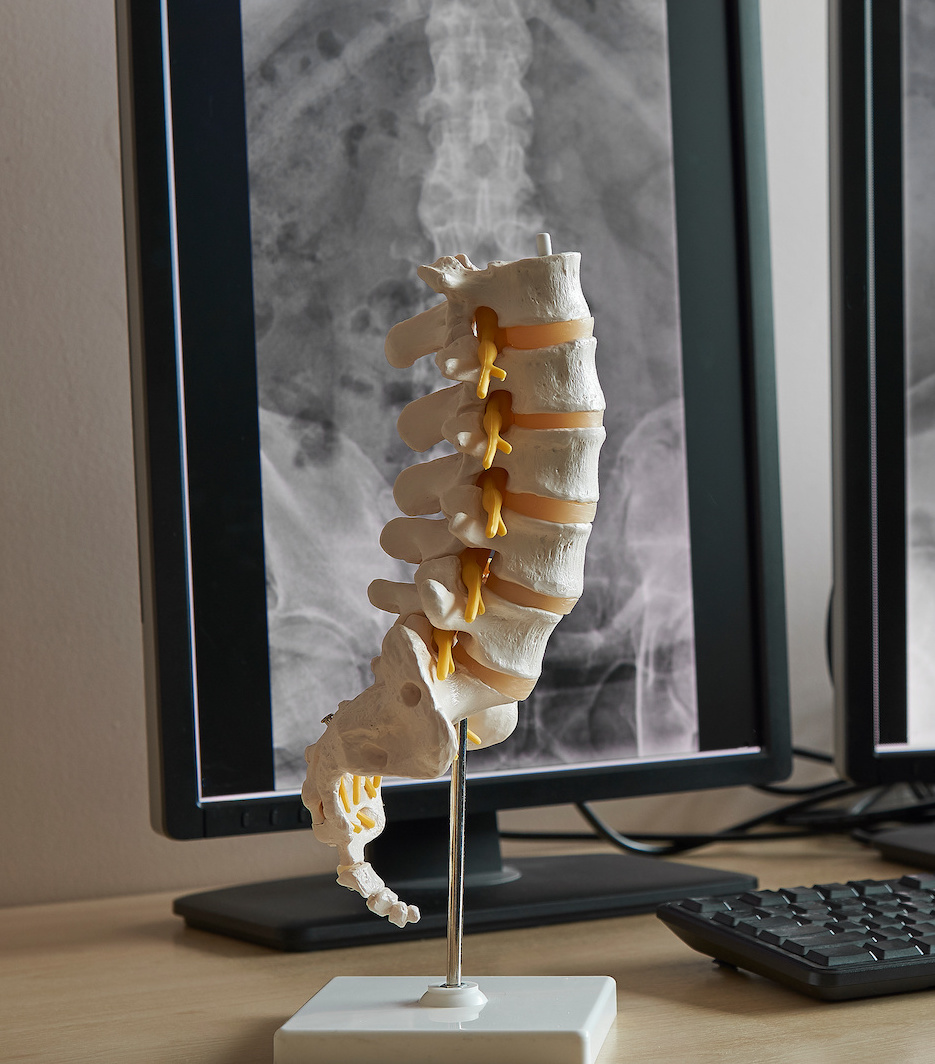
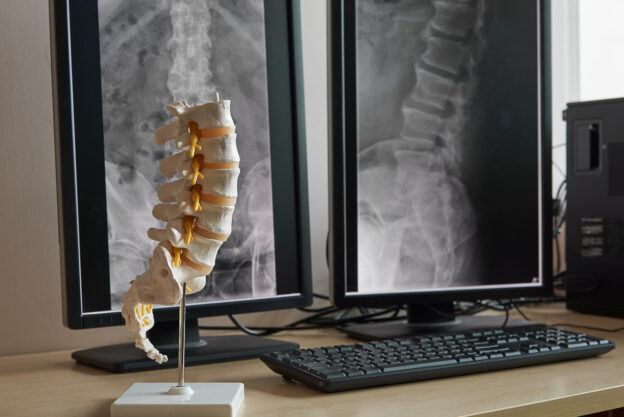
Welcome to
Complete Recovery
Every spine is different, which is why our team is dedicated to continual research and clinical trials to ensure you receive the best care.
Our advanced treatment solutions are tailored to your specific needs, taking into account your age, lifestyle, and comprehensive testing (including MRIs or CT scans where necessary). What we do for you may differ completely from what we do for someone else, even if their source of pain seems similar on the surface. The body responds differently to different treatments, and we need to ensure that we administer the best solution to maximise your flexibility and motion.
Artificial Disc Replacement
Reclaim your life, faster. Chronic pain sufferers choose Artificial Disc Replacement to reverse pain and return to ‘normal’ life sooner, often within a few days. The procedure involves replacing the damaged disc with an artificial device, designed to mimic normal spinal function. It’s safe, effective and changes lives.
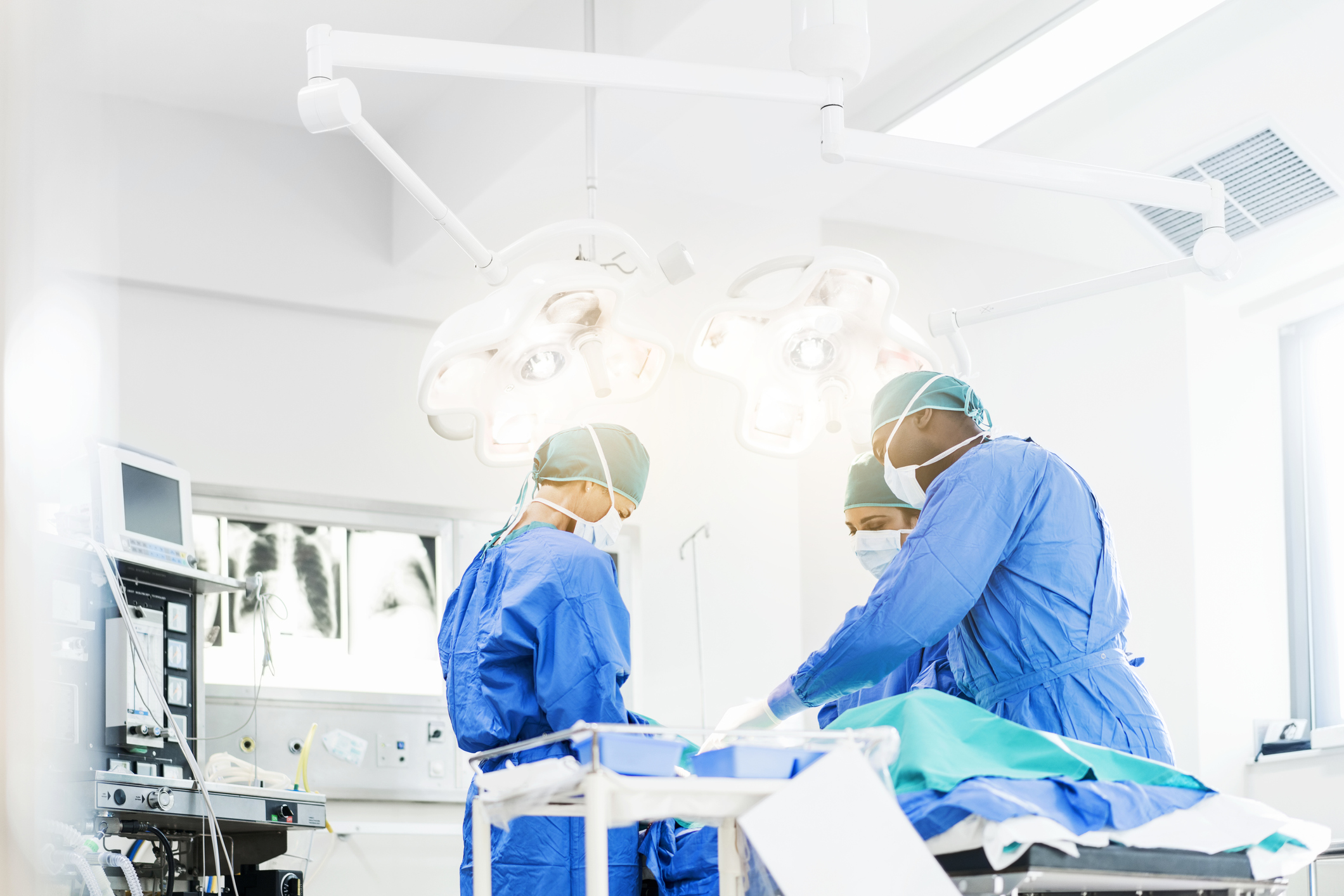

Surgical Procedures
We offer various advanced surgical procedures depending where you’re at in life and what your spinal concerns are. Sometimes pain can seem as though it has a similar cause from one person to the next, but often what is right for one person can be completely different for someone else.
Aging Management
Age is only a number. As technology advances, so too does the aging process, providing us with many different ways to help manage (or slow) it. We can assess where you’re currently at, where you want to be, and create a complete health profile for you, that helps you age slower, and get more out of life.

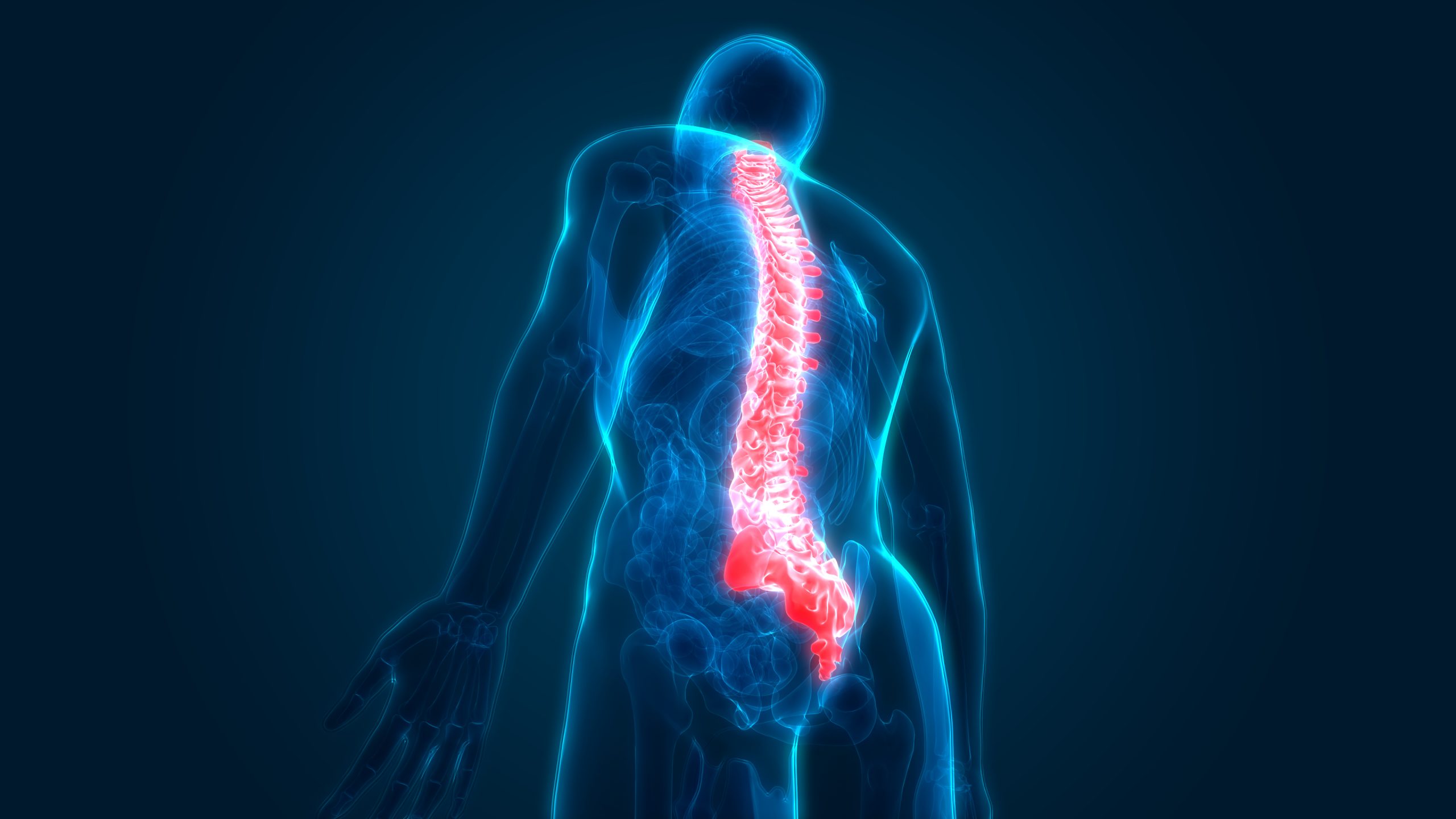
Spinal Conditions
The spine is a complex system made up of 26 vertebrae and 23 discs that house the spinal cord and protect the nervous system. Lifestyle, job roles, sports or aging can all have a negative impact on the spine, resulting in one or several spinal conditions that can impede movement, motion and enjoyment of everyday activities.
4D Health™
The spine controls your entire body and quality of life, which is why we go beyond spine health to assess you from every angle, with our trademarked 4D Health™ system. By taking a holistic view of the way you live your life, you can ensure you make the most of it.

Restorative Motion
Restorative Motion Surgery is an off-label procedure developed by Dr. Todd H. Lanman that restores lost motion due to past or failed spinal fusions. By applying the success of Artificial Disc Replacement to reverse damage and restriction caused by spinal fusion, we have seen compelling results for our patients.

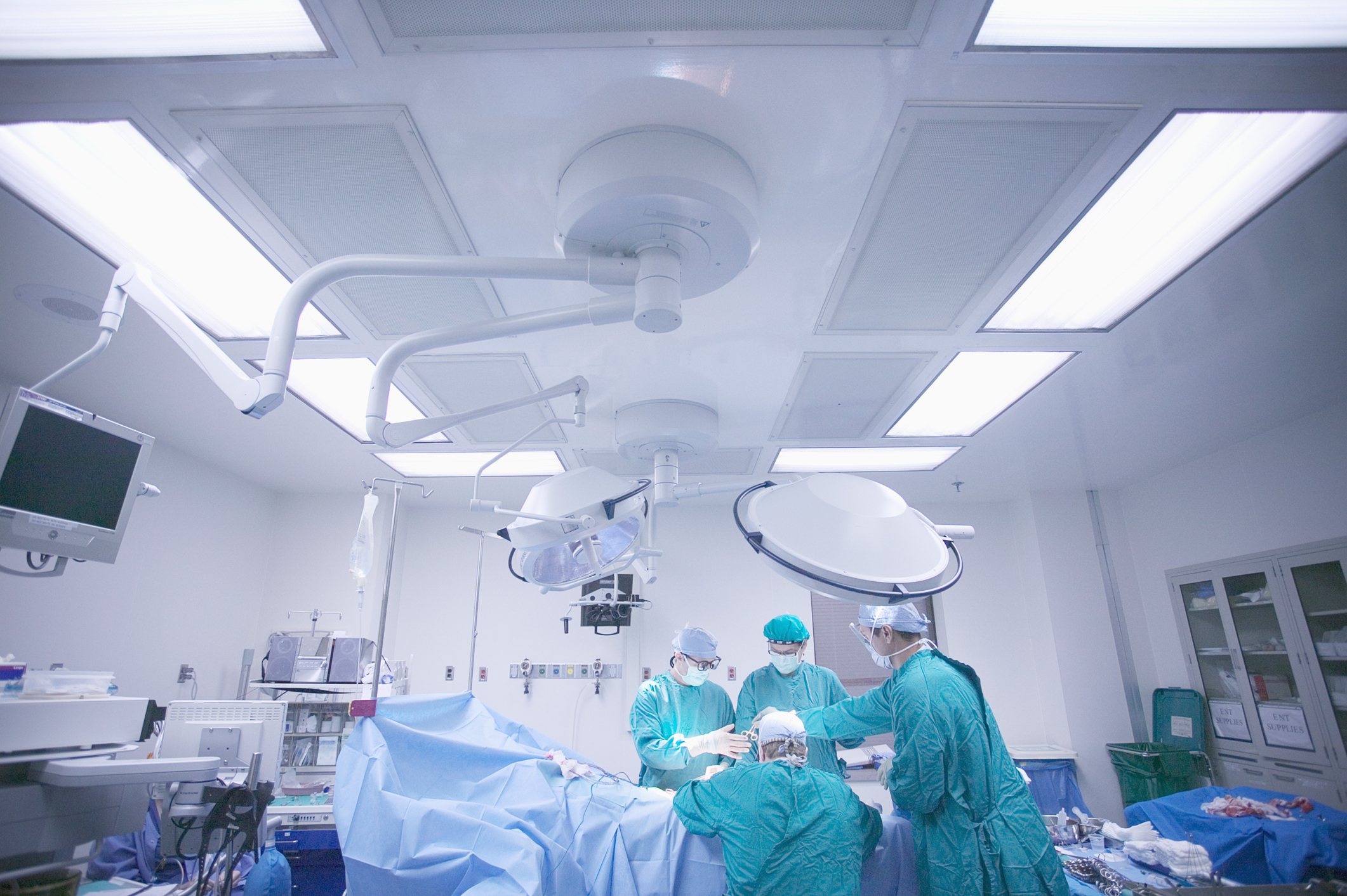
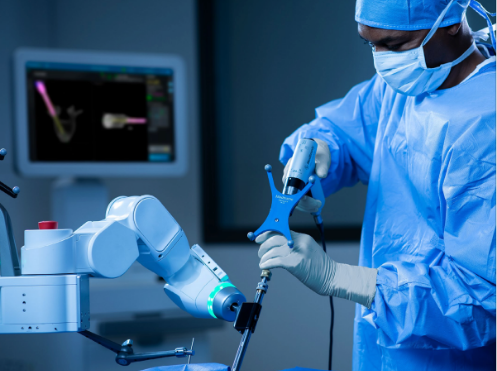
Robotics Spine Surgery
Our commitment to embracing leading-edge technology extends to the operating rooms. We employ superior surgical robotic guidance to ensure enhanced patient care during surgical spinal procedures.
Bone Health
Optimum bone health is essential to successful aging management. It’s also often overlooked by many patients who fail to understand or educate themselves on preventative measures that can help maintain strong, healthy bones later in life.

For the Cervical Spine, click below to learn more about the various surgical procedures offers included:
For the Lumbar Spine, click below to learn more about the various surgical procedures offers included:
Ready to reclaim your life? Get in touch today.
FOLLOW US ON SOCIAL MEDIA | @ADRSPINE